Another installment in my ongoing series explaining why things are the way they are in Dramatica.
The Four Classes: Universe, Physics, Mind, and Psychology
As mentioned in the previous episode of this series, in our efforts to explore how story structure worked, we had early on determined that exploring the psychology of the main character might be the key to unlocking it, for reasons described there.
So, we began looking at many different kinds of stories for anything having to do with the main character’s motivations and manners of thinking, and whenever we found something that described such things, we put it on a post-it note and stuck it to the wall.
Eventually we saw patterns in the notes that had by now absolutely covered the wall in our conference room. For example, we could see that some of theses psychological attribute seemed to be opposite attitudes such as Faith and Disbelief or to represent two ways of looking at things, such as Hope or Fear, or two approaches such as Pursue or Avoid.
So, we organized as much as we could of the notes we’d already gathered into pairs of opposites. When we’d done that, we found we had a lot of single items left. Naturally, we figured that once all the pairs were pulled aside, these remaining single that we had observed in stories probably also had opposites that we just hadn’t noticed or encountered yet. Rather that go looking for them, which would take quite a while, we thought it would be a lot easier just to calculate what the opposite of a single item should be.
Now this is a pretty important decisions because it marked the first time we built a part of the model not just from observation but by extending patterns we had observed into new patterns never directly observed (at least not then, though all these “predictions” have now been verified in thousands of stories).
The notion was, in pulling together the initial pairs from data, we had developed a “feel” for the relationships between the two items. Based on that feeling, we could take any of the single words and determine a pair for it so that the semantic relationship between the two words, between their meanings, would be just like the relationship between the pairs we had already observed.
The development of Dramatica is largely a story of seeing relationships in data, then extending the theory/model to fill in other patterns that were only partially complete.
As we continued, we saw that some of the pairs seemed like a counter-point to another pair, such as the pair of Support and Oppose seemed related to the pair of Help and Hinder – the first pair being more about attitude and the second pair more about action.
So, we started gathering as many pairs as we could into groups of two related pairs. As it turned out, the pairs from data did best as groups of just two pairs. Any more pairs seemed unbalanced – again, based on intuition that story structure ought to be symmetrical. I mean it just made sense, didn’t it? We didn’t know, but it sure seemed that way so far, so we proceeded under that assumption, and having one pair counter-balance another pair played right into that.
We also found that some items that seemed like they were higher level concepts that were kind of like an umbrella word that described the family of two counter-balanced pairs. In other words, our simple groups of four were now beginning to be seen as the children of a parent post-it term. Conversely, the parent terms might be seen as being made up of the two pairs within it – or even perhaps made up of the four items contained in the two pairs.
And then we found that two parents made a higher level pair, and two pairs of parents were topped by an even higher level parent and so on. Now, some of this was from observed data, some was from extending the patterns we found. But all along, we were developing a sense of some underlying relationship that existed just beneath the surface of the patterns – we couldn’t see it, but we could feel it.
In his book about how they discovered DNA, James Watson (of Crick and Watson) describes how they had a feeling based on all the data that DNA might be some sort of helix, but had no proof and also no idea what kind of helix. So, they ordered some molecular models, basically industrial tinker toys, and started assembling them into all manner of helices – singles, doubles, left and right handed, and also how many molecular bonds in each twist – stuff like that.
Eventually, they knocked off all the candidates but one because all the others failed to explain all of what little known hard data they had. And that was the famous double-helix. They were so sure they’d found it, just on the basis of its elegance and simplicity (and the lack of alternatives) that they announced their findings and, fortunately for their careers, they were soon proven right.
But we didn’t know that yet – hadn’t read the book. We were just looking for patterns in the data we gathered from real stories, as seen through the notion of the psychology of the main character.
At some point, and I really can’t provide more information on that because we were constantly striking off in all kinds of directions simultaneously, but at some point, we realized the obvious: stories on not built from characters alone. Duh.
As I recall, we already had some items on post-it notes we’d gathered that seemed more descriptive of plot than of characters or, perhaps, of the material world than of the mental world.
Taking a clue from the hierarchy we were building and expanding for the main character psychology, we took those more external post-it items and started building a companion hierarchy of them.
At first, we worked the external hierarchy’s parents and children independently of the psychology. An then, much to our surprise, we started to see that some items in one hierarchy had a comparative item in the other. For example, Memory in the psychology set had a counterpart in Past in the external set AND in the same relative position in external as Memory was in internal.
Now that pretty much knocked us on the floor. It was looking as if each set was the same as the other, just with a different perspective – one looking out and the other looking in. How? Why?
Perhaps, we speculated, the relationships in each hierarchy represent what we see when we look at anything – all the available perspectives we have available to us. When we look at the external world, we see things colored that way, and when we look inside ourselves, we see the very same things colored another.
But, we didn’t spend too much time getting all philosophic about it – not yet, anyway. We were out to crack the code of story structure and make a name for ourselves – fame and fortune!
Now working with these evolving hierarchies on the wall was getting a bit cumbersome. Everything was spreading laterally across the room. So, Chris being (among his many talents) a graphics guy, started modeling our concepts and understandings in a more accessible form.
At first he tried putting each into a 3 D pyramid with Mind at the top of one and Universe at the apex of the other. We discovered each was a four-sided pyramid because there were always for items in a set of two pairs. And then their parents made two pairs that also made four items and so on. Not making it up, just following the patterns inherent in the semantics of the words on the post-ii notes, originally discovered in stories.
And then we had the pair of Memory and Conscious in Mind and the equivalents of Past and Present in Universe. After some work, we added Subconscious to Mind and Future to Universe. But how could those be equivalent? Well, perhaps, it is in the Subconscious from whence come our desires, which might be based on looking at what we want in the future?
Well, that turned out to be just wrong – at least as stated – but we had no time for that. We were trying to finish the two hierarchies and discover a way to efficiently present them – not to try and understand any of it yet, unless we couldn’t help it.
So, in time we got two pyramids visualized on paper, but they had a lot of problems, just like Crick’s and Watson’s tinker toy models. For one thing, it was beginning to look like the bottom level of each hierarchy was using the same words as in the other hierarchy and in the exact same places, which was just weird: How could the external world and the internal world meet at the exact same things?
To help answer that, we attempted to put the two four-sided pyramids together, base to base. But if things are in the same position at the bottom of each, they can’t possibly meet item to item, because you’ve flipped them over so they are at opposite sides.
Paradox.
So, we tried putting them point to point, but that provided no practical use at all. Finally we just settled on two pyramids, side by side, where the bottom level was exactly the same in each. Didn’t like it, couldn’t do anything about it, and at least it was easy to see equivalencies from one to the other.
Now how did we get from two classes to four? Well as I said earlier, it’s hard to establish a clear linearity of evolution here since we were working on a myriads of things all at once, which muddies the water. But basically, it is as follows:
Within each hierarchy, we had arranged each set of two pairs in what we came to call a “quad.” This was designed as a visualization by Chris so that the most specific or tangible pair was put on a diagonal from the upper left, and the more ethereal of process-oriented was put on a diagonal from the upper right. By doing this consistently, the natures of each pair and their relationship from pyramid to pyramid was easily seen.
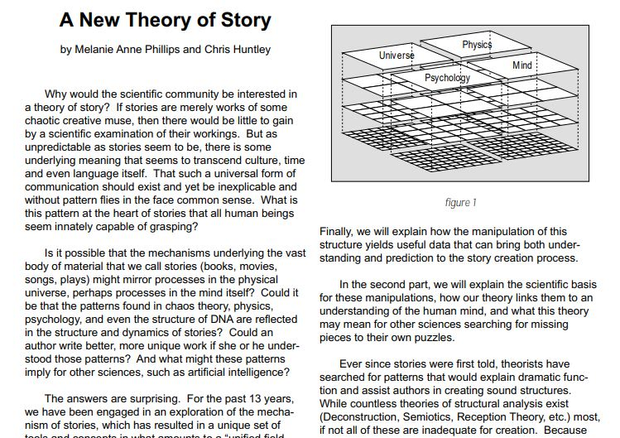
And somewhere along the line, we realized everything in each pyramid was made of quads of four, but the top level only had two items – one pair – Universe and Mind. If story structure was indeed symmetrical, there ought to be four. So what would be the other two? Well, by looking at the relationships of the pairs in the hierarchies at all levels, we were able to determine that the pair of Universe and Mind needed a complimentary pair of Physics and Psychology.
As it turned out, we hadn’t been building a model of psychology but of mind – the tangible pieces of our inner world like Conscious, Memory, and Subconscious. But the processes of the mind, the way it rolled, that would be in a hierarchy of Psychology. And Universe had a process equivalent of Physics.
So, we realized what we were building were four perspectives on the reality that was the same thing at the bottom of each point of view. We called them Classes to give a sciency ring to them.
And Chris, Graphic Man Extraordinaire, converted the pyramids to towers and eventually bound them into the 3D projection we all know and love and the flat table of story elements that holds our hearts to this day.
Again, a lot of things were going on at once, but I think this paints a good picture of where we were coming from and a glimpse at the order in which things happened.
Hopefully, this will help you adopt the same intuitive mind set to guide your logic in continuing to refine and expand the theory.
Comment from Irvaxis, a patron:
Since this post talks about the Table of Elements’ origins, there are some theoretical questions i’ve recently been debating with a friend of mine in regards to its construction. Therefore, here is my question: · In the Table of Elements, at rest, unjustified, does every quad there respect the traditional K A D T arrangement for every term/mental process placed in there, or rather, the K A D T arrangement follows a different logic for each quad, and in such case, which one? This is the closest thing i found to explain it, and it quickly became confusing beyond my comprehension. I was unable to map this onto the entire table: https://www.storymind.com/mental_relativity/mrmath2.htm Thanks in advance like always.
My response:
Hi, Irvaxis. Though I will be doing a “Reasoning” post specifically about the Table of Elements and several about the quad, let me answer your question with a few brief things to consider, and later I’ll hold forth more expansively.
First, the link you included explains part of the issue in the section entitled the non-linear form. It describes (in text and in the included graphic) how the KTAD equation iterates. Let me here address the salient points, not in a “reasoning behind” approach but, for efficiency and clarity, in a “this is what it is” approach.
First, the entire model is a K based system which means that of all the ways you could look at narrative structure, Dramatica was all built from point of view of definitive elements arranged in rigid relationships.
The “why” of this will be covered later, and there are many other ways to build a structure and an engine than this one that addresses the same thing, just as DNA can been seen as a double-heilx or under X-Ray will appear as a crystal. The Table of Story Element is the crystalline version of Dramatica.
Next – the quad is not a thing, it is a visual representation of a logic equation – even an equation of relativity. The primary equation is K/T = AD, which is from a K-base perspective. But the equation itself is designed to describe the relationships among four processes, each represented by one of the four letters, which are the four “bases” of the DNA of narrative.
When the equation iterates is is not just working like traditional iterative equations where the result is then plugged back into the variables of the equation to create expanding fractals. Rather, the quad represents an iteration in which the result of the equation changes the operations in the structure – essentially, changing the position of the variables in the equation but not the nature of the items nor the nature of the equation’s operations, just where specific variables reside in the operation.
Side note: this describes how the mind goes over the same ground again and again, but in different orders through the variables to understand the role of time (sequence) in affecting the results. i.e. : a slap followed by a scream has a different meaning than a scream followed by a slap.
From the top of the Tower of Dramatica, the K perspective (Spatial perspective) is maintained all the way down to the elements, and so, from that perspective, K is always in the upper left and KTAD maintain their relative positions.
But, laterally within the model, the horizontal levels represent the temporal aspect of the iteration, and so, as in the line you included, each quad iterates until it completes creating set of four states of the equation (or if you prefer four iterated equations of KTAD) .
But once that happens at the Type level, to create 16 types (four quads of four), then the temporal process iterates the entire set of 16 types through the same pattern as in the link to create a “chess set” of 64 variations. And so, the tower view has iterated not only horizontally but vertically as well.
As an aside, this is why we say Dramatica is a quad helix, because it is really two helices, each identical to DNA, but wrapped around each other in a super double helix, which reflects in the dynamics as the two different justifications. But finally, we reach the bottom where it all falls apart. There, Quads are broken apart into their original binary pairs and then recombined into new quads in a final iterative operation that takes into account how all four classes are ultimately looking at the same things, but by the time you get into the greatest depth of detail or granularity, the physics of it breaks down.
And at that place at which all four classes come together with the same items but in arrangements that bread the bonds of the physics of it in each of the other three classes, respectively, you are on the edge of atomic dissolution where it interfaces with the quantum realm, and that is the final step before you leave the K based system and move on to the next master perspective.
And when you have iterated through all four master perspectives down to the bottom, collectively, you have arrived at the point where you are no longer looking at structure and the relationships among items, but at dynamics and the influences that alter them – the mythical dynamic model. That is where I am working currently.
Irvaxis:
Let’s see if i got this right so far: · There are at least two perspectives we can hold in the static table of elements (with no component of time/sequence): A vertical one (i assume, top down), and a horizontal one (or also named lateral, which would be within the same floor of the towers). · The vertical view keeps the classic KADT arrangement as the equations themselves are represented with the same bias. · The lateral view of a floor is iterating through the equation positions. I assume this refers to each floor independently. The top floor is the base equation, the next floor is 4 iterations, the next floor is 16 iterations and the last floor is 64 iterations, that iterate according to the rules in that article of yours that i still can’t wrap my head around at this time. · The mix/combination of these two factors decides what the mental process in that place is. Or: · The top down view is the towers/Table of Elements. This is the “spatial” component. This also determines KADT arrangement in this perspective. · The lateral view is the result of justification / is basically for the “time” component. This also determines KADT arrangement in this other perspective. · The Dynamics from the algorithms would operate upon this temporal/lateral side in matching accordance to what’s what on the top down/spatial side. Would it be one of these two? Or something else entirely? Still, i might need a bit of a walkthrough to get how these equations iterate, especially as we go down to the element level, unless that’s planned for a dedicated post. Still, thanks in advance like always.
My response:
Interestingly, all of what you said above “or” is correct and some of what you said below “or” but not all.
For the first point below “or” – Yes, the top down view is the spatial perspective of the mind, which manifests itself in a repetitive KTAD pattern from top to bottom with no iteration.
For the second point – No, the lateral view is not the result of justification. Justification has not happened yet in the model. It is the temporal view of KTAD, unjustified, and from that perspective, the KTAD pattern flows through the iterations, seen as static shifts of meaning in the semantic model.
It can help to think of it this way conceptually – In our minds we have a time sense and a space sense. They do not and cannot see eye to eye. It is like trying to put a plastic ruler down on a pencil that has been laid on a table. If you press one side of the ruler to the table, the other side will move up from the table, like a seesaw. If you press the other side down, the first side will move up. There is not way to make it match on with both sides being down at the same time (though they can both be half-way up.
Down on both sides is a solved problem. Up in any balance between the sides is an inequity in the mind. The mind is driven by inequity and will never be balanced. Self awareness is the interference pattern between space and time. It does not exist within the brain but in the differential between our space sense and our time sense. It is that interference pattern that you see between the top down view, which makes total sense spatially, and the horizontal view, which makes total sense temporally.
But when you put them both in the same space/time construct (the tower) they are incompatible and in place contradictory. And yet they both exist in the same space/time.
It helps sometimes to think of the model without any words in it and without KTAD labels stuck on it. For this perspective the framework of the model appears to make total sense from the top down and total sense from the side across. That is the view from inside out minds because our self awareness cannot view things both spatially and temporally at the same time.
And so, we cannot see the paradox within – it looks good from space, then again looks good from time, then back to space and back to time and everything appears compatible, from the inside. But, from the outside, there is that discrepancy you are beginning to visualize.
Simultaneously, the model is consistent from the top and iterating from the side, which cannot be, yet is. This is expressed in the semantics. Each word in the model was chosen to represent simultaneously the best seesaw compromise between the consistent space down view and the progressive sideways across view. That is built into the matrix of the model itself BEFORE justification.
That is the view from outside the mind, as when we are looking at others, leading to why we say, “If I were you, this is what I’d do,” because from the outside their decisions make no sense. But from inside their minds, your advice makes no sense. As my mom put it to me as a teaching moment when I was young, “People say to me, ‘If I were you, I’d do this…” and I tell them, ‘No, if you were me, you’d do exactly what I’m doing, but if you were in you but in my shoes, you’d do the way you suggested.” Smart woman, my mom.
So, as I say, that paradox is built into the model at rest, BEFORE justification. Now, imagine we can only think at all because of that paradox, and it is the best we can get living inside our minds by virtue of how they are constructed, how they MUST be constructed.
And now in that mind at rest, filled with nothing but ready to operate, life experience enters the picture. In a practical world, we see things happen a certain way long enough and we assume givens – if this, then this, and when this, also this. Then the situation changes, but we are stuck with the givens. (We must adopt givens or we would have to refigure everything we know every time we considered anything at all – bad survival trait for the species. So, we establish givens which become the framework of how we see the world.
And then something changes and those givens don’t work any longer. For example, you understand when to use logic and when to use feelings to solve a problem, but now logic isn’t working any longer because of a different environment. So, you eventually give up on it and go with somebody’s advice to stop over thinking it and just go with your feelings and you do.
That’s the moment logic moves to the back burner for this kind of problem and feeling moves to the front. And now you’ve moved a mental process from its original position in the model matrix to another position in a flip. That is the beginning of the justification process, when something is either flipped spatially, or rotated temporally to adjust to experience altering either its position in the model or its sequence.
But, since time and space are interconnected in the model, when you flip or rotate one thing, the other goes with it and is also altered – space alters time and time space simultaneously. And this is how and when the justification process is applied to the model. It is not contained in the model – that is only the paradox of the interference pattern of space and time that creates self awareness in a mind (or model) at rest, carried to the the nth degree as far into the details as we can see within ourselves before we reach the point where if we look deeper, we lose a level of the upper view – the size of mind constant – so that the model is always the same size, no matter what kind of human issue we are looking at.
And it is upon that model of constant size and built-in paradox at rest that first one justification wind up is applied and then the other, in response to the eight dynamic questions. The final four questions of the total of twelve serve to position that effect upon the model in a particular place, but more on that later.
So, that’s why the model is as it is and where and when justification is applied and does not inherently reside within the model at rest and is not involved in the paradox in the vertical and horizontal levels. Good stopping point for now. 🙂
Irvaxis:
Alright, that is super-clarifying, thanks a lot! I feel like i have the gist of why the algorithm found coded in the patent and the apparent simplicity of “there are only 8 algorithms” seemed to mismatch. I have to ask one more thing, although this may need its own topic sometime: Is there a known representation of the temporal/lateral, unjustified perspective, with the corresponding KADT attachments/iterations? Because if there is, or if it can be created, this might heavily accelerate the process of recovering the algorithms and most especially the theory behind them, i conjecture. Because if these two are implemented as a single piece of code as i suspect, de-coupling them may prove to be crucial to get back the correct understanding of it.
My response:
In fact, I do not know. I was always on the theory side, not on the implementation side, so I’d come up with the concepts and the next thing I know they’d show up working in software. I see what you are saying – that if we could take the iteration “code” out of the software the justification code would remain, sort of. But, as far as I know, the iteration code isn’t in the software at all.
Rather, that’s just the concept that explains why you run into the semantic terms seeming like they don’t follow a strict KTAD pattern in the Table. But there was no need to code that part. All that was needed was the semantic terms that were used and their position in the model at rest, and then to run the two justifications on it.
So, essentially, that whole vertical/horizontal iteration “slip” it encoded in the semantics so that the semantic relationship among the four items in a quad gradually shifts as one moves through the at rest model, indicating the changing nature of KTAD through a gradual change in semantic meaning an the relationships among those altered meanings and relationship due to iterations.
Essentially, I imagine there is a semantic change in nature of the specific words from top to bottom and a change in the semantic distance between the words within quads from side to side across the model. This way, both the alteration in meaning of moving from top to bottom spatially through the four levels KTA and D and the alteration in the nature in the change of the relationships among KTAD within the evolving equations are combined in a single semantic shift, literally word by word. Therefore, both spatial and temporal shifts are unseen in terms of the toward and only contained in the semantic values. As a result, in the program it was not necessary to code either the spatial nor temporal shifts. All that was needed was:
1. Construct the matrix of the table.
2. Assign the semantic terms to their at rest position in the matrix.
3. Twist and turn the model with the two justifications based on the algorithms, including overlaying the PRCO and 1234 with the first and second justifications, which goes first depends on the algorithms.
That’s all that really happens with the model. Then the story point relationship table is overlaid so the engine can narrow the number of storyforms remaining by making choices, thereby providing more information about the structure than the author entered. And then you derive the PRCO and 1234 information and provide that to the author as well.
You know, when I stop to think about it, perhaps my greatest frustration is that to most folks, the elegance of the model is invisible. Of course, for writers, why would they want to bother with that anyway, as long as it works.
But there’s such a hidden beauty there, yet with many people, they perceive the Dramatica quad structure of the tower view as just a bunch of nested cubby holes that are just handy for holding dramatic topics that might show up in stories and have been grouped in quads of similar words.
Of course, as described above, the quads in the tower represent nested iterative equations at four different fractal levels as their variable are altered. And the iteration of the actual operations within each equation, not the variable values but the operations of the equation itself across the horizontal axis of the model CANNOT be included in the tower itself because they cannot co-exist with the top-down fractal approach – those two view are incompatible in the same space-time, must like real and imaginary numbers.
So the words in the model do the job of illustrating the gradual shift of temporal iterations (frictals) in the lateral plane, and in that way they transcend the limitations of the three dimensional representation of space-time in the model to separate out the fourth dimension of time into the semantics. And so, the model is space from the top down, but time in the iterations of semantic meanings laterally.
Now that’s pretty freaking elegant. But the real clincher is that the whole model with the space of the quads and the time of the semantics, both locked together is that they are twisted and turned through the process of justification to represent not the at-rest state of the mind, but the the potential of the mind’s experience-derived inequities, which are manifest in the potentials created through justification.
And then, of course, there is a second justification. One of the justifications occurs in the overall story mind. The other in the mind of the main character.
The main character is our self-awareness that exists without our mind. But our mind is so much more. Self-awareness is our Conscious mind, but there is also our Memory, our Subconscious, and our Pre-conscious.
And so, there is a fractal relationship between the main character and the overall mind, for the main character resides within it, but as an exact structural fractal – one tower of the complete four, a fractal of the totality.
But what’s more is that one justification is a frictal of the other – temporal fractals of one another that operate identically but one before the other. And so they are temporal fractals (frictals).
Finally, have you as of yet seen the quad that is made up of the two fractal structures (main character and overarching mind) and the two frictal dynamics (the first wind up and the second wind up)?
The structural fractals fall into the K and T positions within this master quad and the dynamic ones exist in the A and D positions. Armed with the understandings denoted above, anything within or without ourselves can be described and understood in the most accurate perspective available to us in our existence as the interference pattern between the mental world and the material world.
Perhaps “elegance” is too tame a word for this?